Brand Development, Web Design, and Google Analytics Specialists
Experienced in SEM, SEO, Social Media, and Traditional Media
The Top 11 Benefits of Guest Blogging

* Original article *
Guest blogging is one of the best online marketing strategies you can invest in.
If you want to spread your brand’s message and win the trust of your target audience, start contributing content to other blogs related to your market or niche.
Not convinced you should work hard writing content for someone else’s site?
You should know that guest blogging offers many major benefits – both for your company and you, personally.
Here are the top 11 benefits of guest blogging.
1. Instant Exposure to Targeted Traffic
Regardless if you whether you get a link to your site, contributing to other blogs should pique your audience’s interest. If you manage to write a top-quality post, expect traffic to start flowing to your site once it goes live.
Traffic is the lifeblood of any online business or blog. Something as simple as a guest post can potentially translate into sales if you do it the right way.
Optimize your website’s landing pages, CTAs, and other elements to boost your chances at conversion.
2. Expand Your Personal Network
There was a time when connecting with influencers was extremely difficult. But with guest blogging, the process is now simple.
For example, some websites that accept guest posts foster a community of contributors engaged in related niches. In some cases, you’ll get the chance to take part in an email thread where contributors brainstorm potential topics. You can also collaborate with others for co-authored posts.
Regardless of what the community’s structure in a particular site is, you can always leverage your authorship. Seek partnership opportunities with influencers – from content cross-promotion to expert interviews.
All you need to do is be active in the community. Leave comments, share other posts, or cold-email your prospects. If possible, you can even invite influencers as contributors to your own blog.
3. Stimulate Social Media Shares
Generating social media shares is one way to exponentially extend your online reach. The more shares your branded content gets, the more shareworthy it’ll be in the eyes of your audience.
If you’re submitting a guest post to a blog with plenty of social media activity, then shares should come naturally once your content gets published.
To get the ball rolling faster, consider embedding highly shareable content in your guest post. Infographics, for example, can help you get 3x more engagement in social media than any other type of content.
4. Grow Your Social Media Following
Guest blogging not only increases the amount of social media shares to your content, it can also boost your follower count and accelerate your lead generation efforts.
By contributing to an authoritative blog, you are essentially getting them to vouch for your brand. This makes you look good in the eyes of their followers.
In most guest blogging arrangements, you also get to customize your contributor profile. Here you can include links to your social media accounts.
All these benefits will make it easier to win your target audience’s trust and turn them into active social media followers. Remember to reward them by posting regular updates and sharing useful information that aligns with their interests.
5. Improve Your Online Authority
Modern online marketing is all about authority. Even with the best content in the world, it’ll be difficult to convert your audience into loyal subscribers or paying customers if they don’t trust your brand.
By contributing to other authoritative blogs, you get the chance to prove your credibility as an information source. It will make your target audience realize that you’re someone who’s recognized by trustworthy brands. And as a result, they’ll be more receptive to any value proposition you may present in your own site.
6. Fortify Your Backlink Profile
Most blogs that accept guest posts allow their contributors to leave at least one link to their own site. After all, most of them don’t offer any monetary compensation for your hard work. A brief brand mention or keyword-optimized link is the least they could do to reward your efforts.
Still, even a single backlink from an authoritative blog will greatly benefit your SEO. They make your content more discoverable and indexable to search engines like Google. As much as possible, try to target websites in your own niche to build relevancy.
7. Grow Brand Awareness
Guest blogging is a great way to establish your authority in your niche.
As much as possible, try to share practical tips that aren’t already found elsewhere.
Leverage the opportunity to let them know what your company does and how it would solve problems.
Also, be sure to instill your brand’s voice into every single post you submit. This will make your personal brand more recognizable regardless of where you submit guest posts.
Some popular bloggers, such as Larry Kim, use a conversational and humorous approach to engage readers. They also avoid writing fluff while keeping sentences short and easy to read.
8. Generate Qualified Leads
One of the fundamental steps to a successful guest blogging strategy is picking the right websites.
In addition to niche relevancy, you also need to look for sites that already have a steady stream of traffic. This will help you connect with people who are already interested in what you offer as a business.
Always emphasize an actionable step when developing the page that you’re bringing traffic to. It should be related to the guest post you’ve submitted to the other blog. Otherwise, your link is nothing more than a disruption in your audience’s journey — a waste of time for them and a lost lead for you.
9. Shorten the Sales Cycle
The sales funnel has always been a challenge for content marketers. By distributing content through popular blogs, you are immediately building your target audience’s familiarity with your brand. Thus, you are shortening the sales cycle for your products and services.
Think of it this way: rather than waiting for potential leads to come to your site, you can introduce your brand’s value propositions in your guest posts.
You just need to be smart when picking or pitching topic ideas for your guest posts.
10. Get Useful Feedback from the Community
As a guest blogger, another advantage of being active in the community is that you get to receive insightful feedback from other contributors.
When you talk about strategies, for example, other experts may tune in to share their own ideas through the comments section. As a result, you can further develop or refine your strategy with their suggestions in mind.
To invite contributors to comment, try adding a call-to-action in the conclusion paragraph. You can refer to the end of this post to see how it works.
11. Sharpen Your Content Marketing Skills
Guest blogging requires every area of content marketing to be successful. It requires you to do content research, adopt the right writing voice for a particular audience, perform influencer outreach, and so on.
Remember, the best way to learn content marketing tactics is to deploy them yourself. You can’t just read about them, follow everything to the letter, and hope for the best.
By launching your own guest blogging campaign, you’re positioning yourself for growth in every facet of content marketing.
Conclusion
Guest blogging is, without a doubt, a crucial step for online marketing success. Once you grasp its benefits, give it a shot and see if you can make it work for your brand.
12 Most Inspiring Entrepreneurial & Business Minded Instagram Accounts

1. Create & Cultivate
Created by Jaclyn Johnson as a unique way to encourage women entrepreneurs to go after and achieve their dream careers. The feed is stacked with inspiring women, powerful quotes, and real career advice that’s sure to kick-start your entrepreneurial endeavor.
2. Tony Robbins
The man. The myth. The legend. Tony Robbins is a motivational speaking ninja with actionable business and personal tips to empower people to take control of their lives and accomplish their dreams. As the most recognizable face in leadership coaching, he provides his over 2 million followers with motivational quotes, videos, and stories of men and women impacted by his programs.
3. Small Business Revolution
Each post hones in on an entrepreneur, making their story a stitch in the greater fabric of America’s small business community. Every story is told through photography, film, and the written word.
4. Amy Landino
Thinking of entering the vlog game? Then Amy’s feed is your place to learn how to “vlog like a boss.” As a CreativeLive teacher and boss at Vlog Boss Studios, she shares images of her speaking at various marketing and leadership conferences, motivational tips and quotes, and actionable marketing advice.
5. Peter Voogd
Peter Voogd is the latest young-gun entrepreneur and motivational guru to take center stage. He’s a best selling author and his Instagram should be your go-to for inspirational quotes on entrepreneurship, following your dreams, and learning how to pick up the pieces and move forward when failure strikes.
6. Harvard Business Review
As Harvard’s influential business magazine, its goal is to improve the practice of management. Follow for stories of business life, strategy, and thought provoking topics that are sure to draw spirited conversations.
7. Garyvee
Garyvee has become synonymous with the hustle. As a serial entrepreneur, best selling author, international speaker, and mega-internet personality he has become one the most important and inspirational business leaders of our time. Known for his frank, passionate, and ruthless advice and commentary, followers go to Gary Vaynerchuk for the no holds bar truth (with an expletive or two thrown in there). His account is full of motivational quotes, videos, and honest tips and lessons to help you successfully launch a business.
8. Gabrielle Bernstein
As a motivational speaker, life coach, and New York Times best selling author Gabby Bernstein teaches her followers the power of self-love and a balanced lifestyle. Both much needed in the business world where people neglect maintaining a healthy work-life balance. Her effervescent personality perfectly comes through on her posts with inspiring quotes and pictures from her personal life.
9. 6am Success
With a lofty goal of inspiring 10 million, 6am Success is the source for inspirational quotes and content.
10. Entrepreneur
Entrepreneur Magazine is the premier source for inspiring, informing, and celebrating entrepreneurs. All of the amazing content you love on their website is now jam-packed into their Instagram account.
11. Lewis Howes
We’ve shared about Lewis Howes in the past, letting you know about his hit podcast and awe-inspiring story of struggle and triumph. Through his Instagram, Howes provides amazing free content, powerful motivation, inspirational stories, and videos to help you pursue your passions.
12. Instagram for Business
Confused by the latest algorithm update? Unsure of how to fully utilize Stories for your business? Then follow Instagram for Business for tips on how to best use their platform to boost your business’ marketing goals. You’ll also be incredibly inspired by other influential businesses they regularly post up as examples of using their platform in a creative and impactful way.
Bonus: Above the Fold Agency
Did you know we too have an Instagram account worth following? We share the latest from our marketing blog, inspirational quotes, and expert marketing tips that’s sure to power your work-week.
5 Perks of PPC Advertising for Your Business

There is amazing value in launching PPC advertising because of the major positive impact it can have on your business. As a refresh, PPC means “Pay per Click,” and is a popular online advertising form facilitated through Google Adwords, Bing Ads, Facebook Ads, and Twitter promoted tweets. As the term implies, you only pay when someone clicks on your ad.
What makes PPC great is the ability to reach a targeted audience quickly by selecting who will see your ads, whether through entering specific keywords or demographic characteristics.
If your business isn’t utilizing PPC advertising then you’re losing out on valuable traffic and a revenue generating stream. Here are a few reasons why PPC supports and benefits business:
- Supports business goals
- Low barrier to entry
- Ability to target
- Works with other marketing channels
- Measurable
1. PPC Supports Business Goals
Whether your goals are high-level brand awareness, targeted lead generation, or e-commerce sales PPC has the capacity to contribute to the success of these goals. It’s the most compelling argument for integrating a PPC strategy into your overall marketing strategy.
Really any type of conversion goal can be tracked, making it an incredibly useful tool for driving traffic to complete end goals. However, we caution to start slow, measure and grow big. Start with a simple campaign, measure the results, and depending on the results determined you can spend more money or adjust the audience and keep going.
If you’re already churning out content, use PPC to amplify your content marketing goals. PPC fosters the middle of the funnel through advertising content downloads, giveaways, contest entries, app downloads, newsletter signups, etc. Whatever your set goals, PPC campaigns can be created to effectively support them.
2. Low Barrier to Entry
Very little is needed to get a PPC campaign up and roaring. Compared to traditional media, which has a lag time while waiting for your ad to go to print or your billboard to go up. With an online campaign all you need is a website and something to sell, and you can get your campaign running immediately across a wide net of people to uncover new prospects and customers.
Better yet, much of the work is completely within the platform itself. From research to campaign build out, you’ll require little aside from help setting up conversion tracking, ad graphics, and landing pages.
3. Ability to Target
There are 290 million internet users in the USA alone, and 3.5 billion total across the globe. The numbers are insane when it comes to the amount of people you can reach today with online marketing. PPC provides the ability to reach massive audiences or extremely niche audiences.
Consider your target market: Are they English or Spanish speakers? What are their interests? Where do live? What are their aspirational goals? Are they iPhone or Android users?
The parameters are endless and it’s up to you to determine and figure out the audience that best fits your product or service. Then hit them with an ad they can’t ignore.
4. PPC Complements & Works with Other Marketing Channels
Within your complete digital marketing plan PPC is so important that it can work as the base of all you do. Digital marketing consultant, Alex Chris, summed up perfectly the ways PPC works works exceedingly well with other marketing channels:
You can use dynamic search ad campaigns and let PPC tell you which keywords are a good match for your website.
You can use PPC to test the effectiveness of different keywords so that you know which keywords to target with long term SEO.
You can use PPC as a way to get more installs for your mobile application and strengthen your mobile marketing.
You can use PPC to get more email signups and enrich your email marketing campaigns.
It’s great for local SEO optimization – You can use PPC to drive customers to your shop door or get direct calls from customers looking for products and services in your area.
5. PPC is Measurable
Metrics and relying on data for decisions is vital for success. A major benefit of PPC is that it’s simple to measure, track, and learn from. Just use the Adwords tool with Google Analytics to garner the most robust results.
You’ll uncover an amazing wealth of information about your audience. You can see who is interested, what they’re interested in, and why they may have decided they’re no longer interested. The clearest picture on what kind of traffic and results you’re generating from your budget will be gleaned easily. No other marketing format can provide such immediate and accessible results.
8 Old School Marketing Tactics That Work for Social Media

Link to Original article
Okay, so it’s hard to imagine Don Draper meeting with Bethlehem Steel execs in Sterling Cooper’s top floor Madison Avenue boardroom, telling them to get on Snapchat. But even though we no longer think of typewriters as “technology” or describe TVs as “radios with pictures,” there are plenty of solid ideas from the Mad Men-era of advertising that translate to social media.
So let’s throw it back to a time before #ThrowbackThursday existed for some good old-fashioned advice from the old-school pros.
1. Doing smart, thorough research
In the premier episode of Mad Men, Don Draper trashes an in-house researcher’s report on the psychology of cigarette users and decides to wing a presentation for Lucky Strike executives instead. While Draper pulls it off, not all ad executives were so cavalier.
“Advertising people who ignore research are as dangerous as generals who ignore decodes of enemy signals,” said David Ogilvy, the founder of Ogilvy & Mather who was credited as the “Original Mad Man” and the “Father of Advertising.”
Ogilvy’s experience at Gallup’s Audience Research Institute taught him to value data way before Big Data became a thing. His knack for research-supported copywriting is best exemplified in his headline for a 1960s Rolls-Royce ad, widely considered one of the best auto taglines of all time.

Nowadays, social media marketers looking to emulate the OG Mad Man’s advice should support their strategies with analytics platforms and research-backed ideas.
2. Learning the rules, then breaking them
There are more game changers in the Advertising Hall of Fame than there are rule followers.
“Rules are what the artist breaks; the memorable never emerged from a formula,” said ad exec William Bernbach, creative director who co-founded the agency Doyle Dane Bernbach in 1949.
Bernbach’s “Think Small” campaign for Volkswagen in the 1960s threw out the rulebook for traditional print ads. To sell the compact Beetle to muscle car-crazed Americans, Bernbach’s team departed from convention by picturing a very tiny car on a page filled mainly with blank space. The small idea translated to a big boost in sales and brand loyalty.

Rule breaking may seem trickier on social media, but it’s still possible. BETC’s “Like My Addiction” campaign caught more than 100K Instagrammers by surprise with the reveal that the Parisian “it girl” Louise Delage was a fake account designed to portray a textbook alcoholic. Created for French organization Addict Aide, the initiative demonstrated that it can be difficult to spot signs of youth alcoholism.
3. Avoiding sleazy bait-and-switch tactics
Known as the world’s first female copywriter and the author of the first ad to use sex appeal, Helen Lansdowne Resor was keeping advertising real long before the ad men of the swinging 60s and 70s came onto the scene.
Her conviction that “copy must be believable,” can be found throughout her entire body of work, including her early copywriting for Woodbury Soap Company in 1910. Smooth taglines like “A skin you love to touch,” and “Your skin is what you make it” remained in circulation for decades.

Social media marketers can take Lansdowne Resor’s point in two ways. First, copy should not be too over-the-top or exaggerated, especially since teens are skeptical when it comes to trusting brands. Avoid empty platitudes or superlatives that may arouse doubt.
Second, don’t lie. Millennials are 43 percent more likely than other generations to call a brand out on social media. You dig?
4. Getting right to the heart of things
It’s hard to imagine that the “I ❤ New York” slogan was invented in a pre-emoji world. Sparse in word count and minimal in design, the logo is emblematic of co-creator Jane Maas’ direct approach to advertising.

In How to Advertise, a book Maas co-wrote with colleague Kenneth Roman, she explains, “Commercial attention does not build. Your audience can only become less interested, never more. The level you reach in the first five seconds is the highest you will get, so don’t save your punches.”
The advice is eerily applicable to video marketing in the current digital media ecosystem, where attention spans are running shorter than ever, especially among today’s teenyboppers. You must catch your audience’s attention immediately, or risk losing them entirely.
Check out The Four Key Ingredients of a Perfect Social Video for more pointers on creating punchy video campaigns.
5. Using the right imagery
Inspired by a sea lion performance at a zoo, John Gilroy developed the “My Goodness, My Guinness” for the Irish beer company in the late 1920s. The series depicts a flabbergasted zookeeper prying his beer from the arms of a polar bear, the pouch of a kangaroo and the jaws of a crocodile. And, of course, a toucan.
The humorous misadventures of the zookeeper pop with vibrant colors set against an often-white backdrop. Keen observers point out that it was Gilroy’s uniform use of typography that helped solidify Guinness’ brand image. The popularity of the artwork and consistency of style made it one of the longest advertising campaigns in history.
Using images is a great way to up your social media game, especially since visuals can aid in information retention. Marketers should ensure that photos complement branding and style guidelines. And where possible, add the logo and logotype to the image. Consistency in style is a bonus, but it will help your followers recognize your brand on any platform.
If you don’t have access to artists, photographers, or graphic designers, check out these resources for creating quick and beautiful images for social media.
6. Ditching the one-size-fits-all approach
As the first black man in Chicago advertising, Tom Burrell quickly saw that advertising boardrooms had a diversity problem. Too often, ad execs would create content for white audiences and expect it to have broad appeal. Or, they’d create a commercial for white actors and film a second version with black actors.
After witnessing a number of tone-deaf gaffs and insensitive blunders, Burrell found himself repeating to his colleagues, “Black people are not dark-skinned white people.”
By advocating for tailoring messages for specific communities, he was one of the first to pioneer ethnic micro targeting in advertising. He founded his own agency, Burrell Communications, in 1971 and quickly became the authority on crafting messages for African-American audiences.
In work he did for McDonalds, Burrell reasoned that the company’s slogan “You deserve a break today” sounded too occasional for many African Americans who had a more regular experience with the fast food chain. Instead, he came up with lines like “Sure is good to have around” and “Get down with something good at McDonald’s.”

With Gen Zers forming the most ethnically diverse population in U.S. history, Burrell’s approach is one that social media marketers should put in practice.
Here’s how to find your audience on social media.
7. Knowing that context matters
In 1970, advertisers working for Schaefer beer created a print ad to commemorate the company’s tradition of producing America’s oldest lager. The minimal layout was designed to place emphasis on the year Schaefer’s lager was introduced, with a 10-word tagline reading: “1842. It was a very good year for beer drinkers.”
The two-page ad was placed in a number of popular publications such as LIFE Magazine. But its placement in Ebony Magazine, a publication with a predominantly African American readership, drew criticism.
As Tom Burrell points out in an interview with NPR Planet Money, the year 1842 in the United States was a year many black people were enslaved. “It just screamed insensitivity,” he says. “It was a horrible year for us.”

Getting context wrong can make a brand appear ignorant at best. At worst, it can cause lasting damage to a brand’s image.
Getting context right, on the other hand, can have a positive effect. Wells Fargo adapted its television commercial so that would be optimized for Facebook, where viewers prefer shorter content and may watch videos without sound. To promote the launch of Friends and prove the show’s relevance, Netflix’s Pre-Roll campaign shows viewers a clip related to the YouTube video they’re about to watch.
Social media marketers should shift from cross-posting to cross-promoting, with content tailored to suit each platform.
8. Engaging the audience in a conversation
In the 1950s, American advertising executive Shirley Polykoff’s personal approach to copywriting convinced women across the United States to colour their hair. By posing the question “Does she… or doesn’t she?” in Clairol hair-dye commercials, she reassured women that a hair colouring—then a new fad—could look natural.
“Copy is a direct conversation with the consumer,” she said. Her lingo was so effective that it’s now part of the vernacular: “So natural only her hairdresser knows for sure” and “Is it true blondes have more fun?” Who knows, maybe if she’d worked on a campaign for Rogaine we’d still be using the phrase Chrome Dome.

Besides being concise and memorable, Polykoff does something important in her copy that all modern social media marketers should take note of—she asks a question. Posing questions to your audience is a great way to get followers engaged and increase the visibility of your campaigns, such as Airbnb’s #TripsOnAirbnb campaign.
To get the conversation going on social media, Airbnb asked followers to describe their perfect vacation in three emojis. Not only did the prompt generate hundreds of responses, but Airbnb kept the conversation going by responding to each submission with Airbnb Experience suggestions. Remember, if you want to start a convo, follow-through is key.
More brands have been exploring the opportunities to engage via direct messaging, too. To jumpstart conversations between brands and users, Facebook just introduced Click-to-Messenger ads.
10 Podcasts that Will Ignite Your Entrepreneurial Spirit

Podcasts are increasingly becoming a part of our daily habit. No other platform allows audiences to consume educational content while completing other tasks. Marketers, business owners, and entrepreneurs strive to become greater experts in their fields, and podcasts give them the ability to develop professionally even during their daily commute.
We’ve sifted through the endless marketing, business minded, and self-development podcasts to give you the 10 very best. Each podcast dives into varying arenas of the business world. All sure to provide nuggets you can take with you into your personal and professional life.
Let the boost in productivity and inspiration begin!
1. Gary Vee Audio Experience
An amalgamation of the million different podcasts and audio content Gary Vaynerchuk seems to produce these days can all be found in the Gary Vee Audio Experience. Gary believes the future is voice and audio, and so you can expect full throttle, epic content to inspire your work day and motivate you to launch your dream business you once thought impossible. Prepare yourself for unapologetic straight talk when it comes to his thoughts, interviews, and business advice.
2. Social Media Examiner
The Social Media Marketing Podcast is a top-10 marketing podcast hosted by Michael Stelzner and fellow members of the SME team. Episodes feature success stories and expert interviews from industry leaders to help listeners learn new strategies, and actionable tips to improve their social media marketing. Delivered in 45 min digestible weekly episodes every Friday, it’s your go-to for everything Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and beyond.
3. Smart Passive Income
Who doesn’t relish the idea of making money while you sleep? This is the core concept behind passive income. Of course, there’s plenty of work to be done upfront to get your business soaring, and this is where Pat Flynn steps in. His weekly podcast provides his audience with life-changing strategies and advice for building your online business. Often he interviews business men and women who share their own stories of failure and success.
4. The Joe Rogan Experience
While Joe Rogan is best known for his stand-up comedy and stint as Fear Factor host, he’s also one of the original podcasters that propelled the platform into the colossus that it is today. We included Rogan because of the breadth of guests he interviews on his show. They range from entrepreneurs, musicians, actors, activists, viral sensations, MMA fighters, to political juggernauts. Each with their own knowledge to impart and stories of struggle and triumph to inspire your own journey.
5. The Tim Ferriss Show
As one of the most prolific marketing and business podcasts on the airwaves, The Tim Ferriss Show has consistently been the #1 business podcast on all of iTunes, and has regularly ranked #1 overall amongst 300,000+ podcasts. Each long-form and content packed episode features world-class performers, entrepreneurs, and business leaders to extract the precise tactics, tools, and routines they use so you can adopt into your own life. It’s definitely a can’t-be-missed listening experience.
6. Online Marketing Made Easy
If you’re a small business then you have to listen to Amy Porterfield’s Online Marketing Made Easy. She outlines various marketing strategies by breaking them down into manageable, step-by-step pieces. Ensuring she’s fulfilling her mission to make everything as actionable and profitable as possible. Not only does she provide marketing guides, but also killer expert interviews and intimate behind-the-scene secrets from her biggest launches.
7. The Turnaround – The Growth Show
Half of all businesses fail after five years, and only a third make it to 10. Produced by Hubspot, The Turnaround/Growth Show is a podcast highlighting companies that nearly closed up shop, and instead embarked in a stellar turnaround. Making it a great show for any business struggling with how to grow effectively.
8. The School of Greatness
Hosted by entrepreneur and internet guru, Lewis Howes, The School of Greatness is dedicated to sharing inspiring stories from the most brilliant business minds, world class athletes, and influential celebrities to discover what makes people great. Prepare to self-analyze and feel tested. Both of which will lead to self-growth and success.
9. The Broad Experience
The Broad Experience is a 20 minute podcast conversation about women, the workplace, and success. Hosted by Ashley Milne-Tyte explores everything from race and class to being a professional woman without kids, the difficulty of delegating, and sexual harassment. Outlets like Fortune, Gawker, The New York Times, The Economist, The Guardian and more have praised the show for its storytelling and intelligent discussions.
10. Entrepreneurs on Fire
John Lee Dumas has taken the term “content creator” to the next level. His podcast, Entrepreneurs on Fire (EOF), interviews inspiring and successful entrepreneurs 7 days a week! Everyday you’ll hear from featured guests describing their worst entrepreneurial moments, their AH-HA moments, and what’s working for them in business right now. Over 1,900 interviews have been published with guests ranging from Tony Robbins, Seth Godin, Gary Vee, Barbara Corcoran, and many more.
Email Marketing Segmentation Strategies that Grow Your Business
Email marketing segmentation is a huge boon for businesses. Marketers know segmenting emails into various groupings not only improves open rates, but also click-through rates that ultimately lead to conversions.
Recent data provided by Mailchimp reveals that segmented campaigns receive 14.31% more opens and 100.95% more clicks.
Now more than ever, segmentation is proving to be a greatly effective strategy for businesses looking to drive customer engagement and sales.
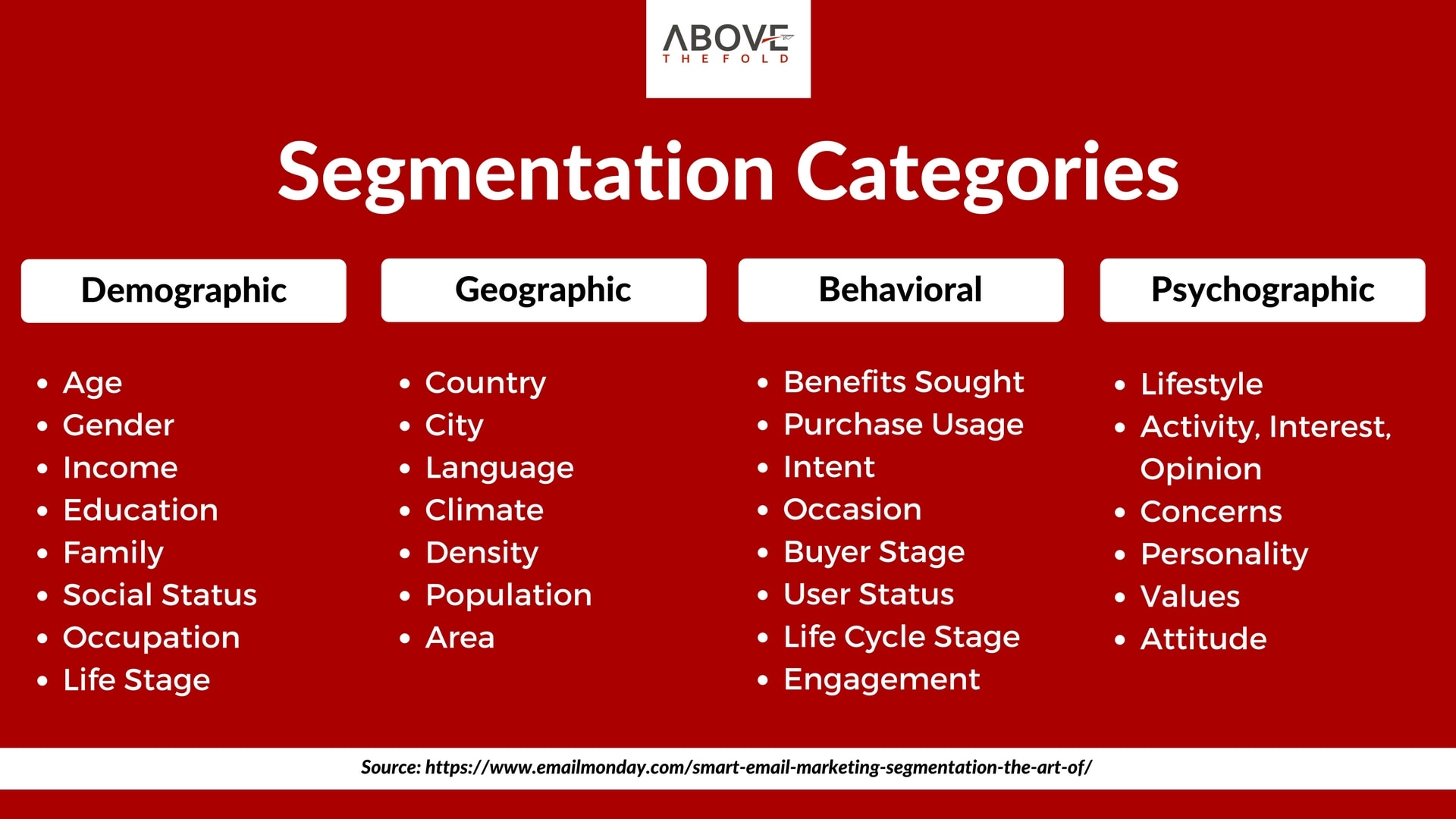
It’s All About the Group
Email segmentation is all about the group, and the art of positioning subscribers into groups based upon different factors like: behavior, interests, age, gender, location, and so on. Depending on your industry and goals, the factors will adjust accordingly.
According to DMA, marketers have found 760% increase in email revenue from segmented campaigns. This begs the question, if all your subscribers are different, why are you treating them like they’re all the same?
Established groups should be diverted into buckets fitting the factors you’ve outlined that then serve them specific and curated content and offers they’re most likely to take an action on.
What’s even cooler about segmentation is you can tap into your subscriber’s aspirational self, and not just target based upon where they are in their customer lifecycle. A tactic expertly used by luxury brands.
Segmentation Strategies:
Before dividing up your contact list it’s important to understand a few different proven segmentation strategies. In fact, these are strategies you can immediately adopt today so you can start seeing results tomorrow.
1. Demographics
Demographic data is your launching pad for segmenting your email subscribers into specific lists. Demographic data includes factors like age, gender, income level, company position, education, etc. Seemingly simple demographic data can tell you a great amount about your customer’s wants and needs, and therefore how you can serve them and even turn them into raving fans.
Our recommendation is to acquire as much demographic data from your customer upfront, without scaring them off of course. Whether they’re filling out a form to sign up for your newsletter or are in the purchase process, this is your opportunity to start them off correctly in your email funnel.
For example, if you’re an outdoor retailer, gender is probably at the top of your list so you know which products to suggest to your customers. If you’re a marketing consultant, then knowing your customer’s job title is valuable.
What metrics are the most integral for you business? Be sure to include these in your customer’s signup process.
2. Email Engagement
What better way to sort your customers than by the way they interact with the messages you’re already sending? Segmenting based on email engagement is a simple and effective method that will have a major impact on your results.
Thankfully email marketing services already do a bit of the leg work for us by providing open and clickthrough rates on each email you send. With these metrics you discover your active vs. inactive users.
An inactive user would be someone who hasn’t open an email in three months or more. This is a customer you want to bring back into the fold. Tailor a campaign to re-engage them, whether through a discount offer or a “hey we haven’t seen each other in awhile, check out what’s brand spanking new” type message.
Conversely, you can reach out to your customers that are highly engaged and repeat buyers. We’d call these people your fans. Announce to your fans about an upcoming sale that they’re receiving exclusive first-access to since they’re a loyal customer. If they clickthrough then mark them as “interested” or whatever label you deem appropriate. Then you can develop a specialized campaign to further target them as consistent (maybe even reliable) buyers.
3. Geographic Area
For businesses where geographic location makes a big impact on purchasing decisions then segmenting based on geographic location data is paramount.
A great example of a brand doing this right is Spirit Airlines. Every customer that uses Spirit must filled out basic information like sex, age, and address. The address category is what allows Spirit to target its customers based upon location.
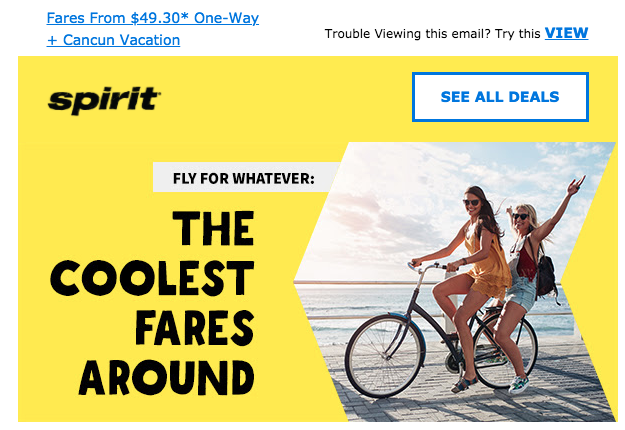
If you’re living in San Diego, why would you care about flight deals out of Denver? You wouldn’t. And this is why geographic location data segmentation is powerful.
Spirit is able to target and supply customers with information, deals, and fun trip facts based upon where you live and where you’re headed. Thus driving open rates and engagement.
Here are a few more examples of ways to use geographic data:
- Location-specific content: Offer a personalized experience by including a specific location in your headline and/or content
- Advertise regional promotions: Offering a Pacific Northwest specific sale? Send focused emails for this promotion to customers in the region.
- Time-based: Send out email at optimum times for customers in different time zones
4. Personal Interest
This is where it gets a little trickier, however if you can pull it off it will greatly help with granular segmentation strategies. You can gain information on your customer’s personal interests by creating user profiles on your website or by using an email subscription center where they can tick off their purchasing or information interests.
You can invite them to do this either in the signup process or encourage them down the road in follow up emails to complete their profile online. Having this information is an amazing tool to help you target customers effectively, and avoid wasting their time with let’s say tech products when their only interest is in beauty products.
In conclusion, email marketing is a highly effective tool that when used correctly can not only nurture your current customer base, but also grow it to unprecedented levels. All you need is a simple email marketing service, knowledge of your customers, creativity, and the drive to build out these segmentation strategies.
Here are a few email marketing services we recommend:
Contact us to learn how we can help your business with email marketing strategies!
The Ultimate Guide to Small Business Goal Setting for 2018

15 Resources for Effectively Setting and Achieving Goals in Your Small Business in 2018.
Every single small business owner, in any stage of the business life cycle, needs goals to keep moving forward, get them motivated to do more, and maintain the success of their businesses. Goal setting can follow many different processes, and each one can be successful as long as it defines the long- and short-term goals and devises a plan for getting there.
Here is a collection of resources that will help you maximize your process and guide you as you achieve your business goals, from the simplest to the most ambitious goals on your list.
Getting Started with Goal Setting

There’s no denying the importance of business goals. Goals provide direction, motivation and a clear way to measure your progress. Without goals, you may struggle to find the path from where you are right now to where you want to be.
The tips in this article will help you get started with goal setting for your business, focus on the specifics of what you hope to accomplish, and start to put your plan into action.
30 Minute Goal Setting Cheat Sheet
It doesn’t have to be a long and complicated process. You just need to pick a theme, identify the necessary action items and make a commitment to the process. If you have just 30 minutes, you can follow these four simple steps to create a goal for your small business.
SMART Goal Setting 101
Whether you have a 50-employee company or an empire of one, your business success depends on your ability to set and achieve goals. This article will introduce you to the concept of SMART goal setting and help put your business on the fast-track to goal setting and achievement.
7 New Year’s Resolutions that Will Change Your Small Business
New Year’s resolutions can be a powerful way to kickstart goal setting. A resolution, after all, is a decision to do something differently to bring about positive change. This article outlines seven possible resolutions you should set this year.
3 Easy Steps for Turning Your New Year’s Resolutions Into Powerful Goals

A resolution on its own is meaningless. It’s when you create a plan that focuses on the desired results of your decision that the magic happen. These three easy steps will help you turn your resolutions into goals you can focus on in your business.
4 Common Small Business Goals to Inspire You
If you’re having difficulty identifying the right business goals for you, this article is the one you should read first. While there are many different business goals you can set, sometimes the most common are also the most relevant.
This article looks at four common business goals and provides a number of resources that will inspire you to get started.
5 Common Small Business Goal Setting Mistakes
Avoiding mistakes can save you a significant amount of time and effort down the road. So in order to make your goal setting as efficient as possible, this article lists five common goal setting mistakes you should try to avoid in your small business.
How to Reach Your Biggest, Most Pivotal Goals

The only way to make goals count is to give them the attention they deserve. Here are some tactics to use this year as you set new goals and commit to seeing them through to fruition.
Backward Goal Setting
When you are overwhelmed by the idea of setting goals, it can be helpful to start at the end and work backward. This tutorial will walk you through the process of creating realistic goals that are broken down into single actions you can focus on one at a time.
How to Set Business Goals with Just One Word
Creating a goal with just one word is a way to eliminate the overwhelming part of the goal setting process and focus on a specific theme. Here’s how to start.
Goal Setting & Tracking Apps

Having a system for setting and tracking your goals is an important part of the goal setting process. Without a system, it would be impossible to identify a goal, create an action plan and track your progress.
This list of goal setting and tracking software will help you create, track and achieve your most important business goals.
10 Powerful Goal Setting Steps
Envisioning your ultimate business goal may not be that difficult, especially if you are a driven and determined business owner. Figuring out how to achieve that ambitious goal, though, can be another story.
Returning to the basics of the goal setting process is one way to get and stay on track with your business goals, and getting motivated and inspired is another. This article focuses on both.
Tips for Successful Goal Setting & Achievement
There are a lot of moving parts when it comes to goal setting. The good news is that you can do a few things that will help you create an environment that is conducive to goal setting success. Taking the time to work on the items listed in this article will help reduce the challenges that come with tackling your biggest goals.
How to Get & Stay Motivated
Without the motivation to work hard and overcome challenges, you may find yourself in a slump, and worse, you may lose your passion for achieving your goals. Motivation is vital for any goal setting process; without it, it will be very difficult to reach your goals.
Review these tips for getting and staying motivated when you’re striving to accomplish your goals so you can build momentum and push through challenges with ease.
6 Alternatives to Traditional Goal Setting
Sick of traditional goal setting? Try one of these six alternatives that can help you create a new focus and intention in your business for the coming year.
If you’re interested in speaking to us about how we can help you achieve your marketing goals this next year please contact Matt at matt@abovethefoldagency.com. Cheers to a successful and prosperous 2018!
iPhone X vs Pixel 2 XL: Which One is Right for You?
With the anticipated release of the iPhone X it has many thinking, is the crisp OLED screen and Face ID technology worth the hype and biting the $999 bullet? We’re looking past the hype and sticking to the straight up facts.
Now we haven’t personally tested the iPhone X and Pixel 2 XL, however we compiled all the important specs and testimony from journalists who have spent time with each phone. Thereby giving an unbiased view behind the hardware, design, and capabilities.
From there you can decide for yourself, are you team Apple or team Android?
The Specs You Need to Know
To the average smartphone user it’s difficult to fully grasp what the tangible differences are between the iPhone X and Pixel 2 XL. So we created this handy dandy cheat sheet for your reference, and even included the iPhone 8 as your cheaper powerhouse alternative to the shiny new toys in the market.
![]()
Design Differences
The iPhone X’s design is so beautifully crafted that if Steve Jobs were here today, he’d give it a standing ovation. Aesthetically, the Pixel 2 XL leaves much to be desired.
iPhone X: The notch, the section at the top of its display that holds the camera, has received a bit of flack for its encroachment into the screen. Despite the necessary evil that is the notch, the overall design is seamless, crisp, and a full 360 degree beauty. The back is made of glass to allow for wireless charging, and the stainless steel sides give it the grip it needs.
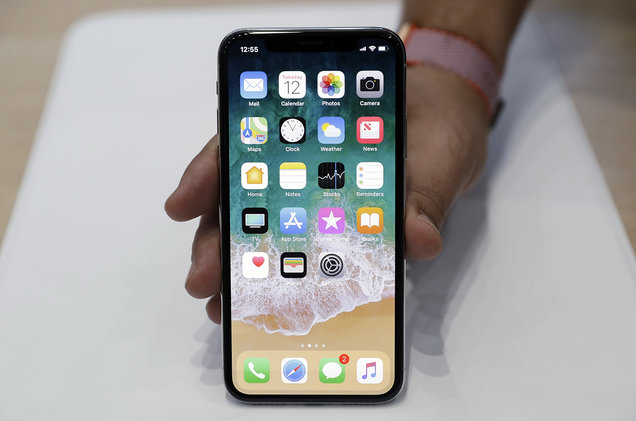

Pixel 2 XL: As is the case with the majority of Android phones, the overall design feels rather uninspired. It features a two-toned aluminum back with a satisfying grainy feel that’s sure to provide excellent grip.
![]()
Both chose to continue the trend away from a headphone jack, forcing users to adopt a wireless lifestyle or adapters (just don’t lose it!). Apple and Google’s phone’s use different charging cables. Lighting or wireless for iPhone, and USB Type-C for the Pixel.
OLED Comparison
Apple has finally moved to OLED, a feature Android beat them to when Samsung released their Galaxy S II.
iPhone X: Apple’s screen is a 5.8in display at an extra tall 19.5:9 aspect ratio, and at 2436×1125 (458 pixels per inch), it’s a step up from the already-crisp iPhone 8 Plus panel (a 5.5in 1080p LCD).
It’s an exceptionally bright phone, emitting up to 574 nits, which helps the iPhone achieve much wider viewing angles. Additionally, it offers more accurate hues; it registered a Delta-E score of 0.21 (0 is perfect).
Pixel 2 XL: Google has Apple beat on sharpness, with its 6in, 18:9 OLED display coming in at 2880 × 1440 (538 ppi). The brightness sits at 438-nit and registered a Delta-E score of 0.28.
Recent concerns over the Pixel’s OLED burn-in has led Google developers to swiftly remedy the issue. Google claims its November 6th update will fix the issue with the introduction of a “fade out” for the on-screen navigation buttons and an adjustment to the screen’s brightness.
Performance
What’s behind the chart? iPhone X’s A11 Bionic processor took only 42 seconds to transcode (convert) a two minute 4K video in the Adobe Clips app. Pixel 2’s Snapdragon 835 chip took an additional 1:13. A time different that’s difficult to ignore.
Camera Capabilities
According to Tom’s Guide’s testing, “The Pixel 2’s and iPhone X’s cameras are both great, but each has its own strong suit.” While Stuff.tv is fully team Pixel with the claim that “Shots are realistic and packed with detail, cramming in loads of dynamic range. The results don’t look overwhelmingly sharpened or too-vivid-to-be-true: they just look phenomenal and lifelike.”
iPhone X:
- 12MP shooters (f/1.8 wide angle and f/2.4 telephoto)
- 2x optical zoom from dual rear cameras
- Captures more natural skin tones
- Optical image stabilization
- Better low-light shooting
- Better HDR shooting
- Portrait mode
Pixel 2 XL:
- Superior low light photos
- Portrait mode
- Portrait lighting feature
- 12MP f/1.8 back camera
- Optical and electronic image stabilisation
- Dual-pixel PDAF
- Laser-assisted focusing
- Crisp vibrant colors
- Digital zoom
Battery Life: Which one lasts longer?
On the Tom’s Guide battery test (continuous web surfing over LTE), the iPhone X lasted 10 hours and 49 minutes. The Pixel 2 XL lasted for 12 hours and nine minutes, leaving the iPhone behind by over an hour. Giving Google’s phone the ultimate endurance.
Special Features
Both phones offer their own range of special features. Whether you’re more keen on higher level security or daily assistance, these phones have exactly what you want, and what you may realize you need.
iPhone X: Apple has taken biometric security to the next level with its Face ID feature. Face ID scans all dimensions of your face, and if it’s a match the phone will unlock. This same technology is used for Animoji, cute and impressive characters that come to life based on your expressions and voice.

Pixel 2 XL: The big winning feature is Google Assistant. It’s the smarter faster version of Siri that’s not easily confused by your queries. And all you have to do to summon Google Assistant is to squeeze the bottom of the phone.
So what’s the bottom line? The race between iPhone X and Pixel 2 XL is neck and neck. To make the ultimate decision it may come down to price, aesthetic, or even the need to be an Animoji. We’ve given you the facts, now it’s decision time.
The Top 99 Marketing Terms You Should Know

Above The Fold Agency thought it was time to provide a holistic marketing glossary – Here are the top 99 terms that are imperative to anyone learning about marketing. We hope this helps you through your journey…
A
1) A/B Testing
This is the process of comparing two variations of a single variable to determine which performs best in-order-to help improve marketing efforts. This is often done in email marketing (with variations in the subject line or copy), calls-to-action (variations in colors or verbiage), and landing pages (variations in content).
2) Analytics
Analytics is essentially the discovery and communication of meaningful patterns in data. When referred to in the context of marketing, it’s looking at the data of one’s initiatives (website visitor reports, social, PPC, etc.), analyzing the trends, and developing actionable insights to make better informed marketing decisions.
3) Application Programming Interface (API)
APIs are a series of rules in computer programming, which allow an application to extract information from a service and use that information either in their own application or in data analyses. It’s kind of like a phone for applications to have conversations — an API literally “calls” one application and gets information to bring to you to use in your software. APIs facilitate the data needed to provide solutions to customer problems.
B
4) B2B (Business-to-Business)
An adjective used to describe companies that sell to other businesses. For example, Google and Oracle are primarily B2B companies.
5) B2C (Business-to-Consumer)
An adjective used to describe companies that sell directly to consumers. For example, Amazon, Apple, and Nike are primarily B2C companies.
6) Blogging
This is short for web log or weblog. An individual or group of people usually maintains a blog. A personal blog or business blog will traditionally include regular entries of commentary, descriptions of events, or other material, such as photos and video.
Blogging is a core component of inbound marketing, as it can accomplish several initiatives simultaneously — like website traffic growth, thought leadership, and lead generation. It does not, however, do your taxes.
7) Business Blogging
Business blogging retains all the attributes of “regular” blogging, but adds a tasty layer of marketing strategy on top. It helps marketers drive traffic to their website, convert that traffic into leads, establish authority on certain topics, and drive long-term results.
When blogging for a business, marketers should create posts that are optimized with keywords that their target audience is searching for and provide helpful, educational material to these readers. Typically, these blog posts should be actionable (by providing an opt-in, downloadable offer), as to provide a metric for the effectiveness of the business blogging.
8) Bottom of the Funnel
The bottom of the funnel refers to a stage of the buying process leads reach when they’re just about to close as new customers. They’ve identified a problem, have shopped around for possible solutions, and are very close to buying.
Typically, next steps for leads at this stage are a call from a sales rep, a demo, or a free consultation — depending on what type of business is attempting to close the lead.
9) Bounce Rate
Website bounce rate: The percentage of people who land on a page on your website and then leave without clicking on anything else or navigating to any other pages on your site. A high bounce rate generally leads to poor conversion rates because no one is staying on your site long enough to read your content or convert on a landing page (or for any other conversion event).
Email bounce rate: The rate at which an email was unable to be delivered to a recipient’s inbox. A high bounce rate generally means your lists are out-of-date or purchased, or they include many invalid email addresses. In email, not all bounces are bad, so it’s important to distinguish between hard and soft bounces before taking an email address off your list.
10) Buyer Persona
A semi-fictional representation of your ideal customer based on market research and real data about your existing customers. While it helps marketers like you define their target audience, it can also help sales reps qualify leads.
C
11) Call-to-Action
A call-to-action is a text link, button, image, or some type of web link that encourages a website visitor to visit a landing page and become of lead. Some examples of CTAs are “Subscribe Now” or “Download the Whitepaper Today.” These are important for marketers because they’re the “bait” that entices a website visitor to eventually become a lead. So, you can imagine that it’s important to convey a very enticing, valuable offer on a call-to-action to better foster visitor-to-lead conversion.
12) CAN-SPAM
CAN-SPAM stands for “Controlling the Assault of Non-Solicited Pornography and Marketing.” It’s a U.S. law passed in 2003 that establishes the rules for commercial email and commercial messages, it gives recipients the right to have a business stop emailing them, and outlines the penalties incurred for those who violate the law. For example, CAN-SPAM is the reason businesses are required to have an “unsubscribe” option at the bottom of every email.
13) CASL
CASL stands for “Canadian Anti-Spam Legislation.” It’s a Canadian law passed in 2013 that covers the sending of “commercial electronic messages” that may be accessed by a computer in Canada. CASL covers email, texts, instant messages, and automated cell phone messages sent to computers and phones in Canada.
14) Churn Rate
A metric that measures how many customers you retain and at what value. To calculate churn rate, take the number of customers you lost during a certain time frame, and divide that by the total number of customers you had at the very beginning of that time frame. (Don’t include any new sales from that time frame.)
For example, if a company had 500 customers at the beginning of October and only 450 customers at the end of October (discounting any customers that were closed in October), their customer churn rate would be: (500-450)/500 = 50/500 = 10%.
15) Click-Through-Rate (CTR)
The percentage of your audience that advances (or clicks through) from one part of your website to the next step of your marketing campaign. As a mathematic equation, it’s the total number of clicks that your page or CTA receives divided by the number of opportunities that people had to click (ex: number of page views, emails sent, and so on).
16) Closed-Loop Marketing
The practice of closed-loop marketing is being able to execute, track and show how marketing efforts have impacted bottom-line business growth. An example would be tracking a website visitor as they become a lead to the very last touch point when they close as a customer.
17) Conversion Path
A conversion path is a series of website-based events that facilitate lead capture. In its most basic form, a conversion path will consist of a call-to-action (typically a button that describes an offer) that leads to a landing page with a lead capture form, which redirects to a thank you page where a content offer resides. In exchange for his or her contact information, a website visitor obtains a content offer to better help them through the buying process.
18) Content
In relation to inbound marketing, content is a piece of information that exists for the purpose of being digested (not literally), engaged with, and shared. Content typically comes in the form of a blog, video, social media post, photo, slideshow, or podcast, although there are plenty of over types out there. From website traffic to lead conversion to customer marketing, content plays an indispensable role in a successful inbound marketing strategy.
19) Content Management System (CMS)
A web application designed to make it easy for non-technical users to create, edit, and manage a website. Helps users with content editing and more “behind-the-scenes” work like making content searchable and indexable, automatically generating navigation elements, keeping track of users and permissions, and more.
20) Content Optimization System (COS)
A COS is basically a CMS (Content Management System), but optimized to deliver customers the most personalized web experience possible.
21) Context
If content is king, then context is queen. Serving up valuable content is important, but ensuring that it’s customized for the right audience is equally (if not more) important. As buyers become more in control of what information they digest (again, not literally), it’s important to deliver content that’s contextually relevant.
22) Conversion Rate
The percentage of people who completed a desired action on a single web page, such as filling out a form. Pages with high conversion rates are performing well, while pages with low conversion rates are performing poorly.
23) Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO)
The process of improving your site conversion using design techniques, key optimization principles, and testing. It involves creating an experience for your website visitors that will convert them into customers. CRO is most often applied to web page or landing page optimization, but it can also be applied to social media, CTAs, and other parts of your marketing.
24) Cost-Per-Lead (CPL)
The amount it costs your marketing organization to acquire a lead. This factors heavily into CAC (customer acquisition cost), and is a metric marketers should keep a keen eye on.
25) Crowdsourced Content
Creating your own content can take more time than you have to lend to it — which is where crowdsourcing comes into play. Allowing subject matter experts, customers, or freelancers to create your content for you is a prime way to get more quality content published in less time. Compile the content you get back into a really awesome offer and give credit to all the contributors — a win-win for everyone involved.
26) Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Your total Sales and Marketing cost. To calculate CAC, follow these steps for a given time period (month, quarter, or year):
- Add up program or advertising spend + salaries + commissions + bonuses + overhead.
- Divide by the number of new customers in that time period.
For example, if you spend $500,000 on Sales and Marketing in a given month and added 50 customers that same month, then your CAC was $10,000 that month.
27) Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
A set of software programs that let companies keep track of everything they do with their existing and potential customers.
At the simplest level, CRM software lets you keep track of all the contact information for these customers. But CRM systems can do lots of other things, too, like tracking email, phone calls, faxes, and deals; sending personalized emails; scheduling appointments; and logging every instance of customer service and support. Some systems also incorporate feeds from social media such as Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, and others.
28) CSS
CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets, and it’s what gives your entire website its style, like colors, fonts, and background images. It affects the mood and tone of a web page, making it an incredibly powerful tool. It’s also what allows websites to adapt to different screen sizes and device types.
D
29) Dynamic Content
A way to display different messaging on your website based on the information you already know about the visitor. For example, you could use Smart CTAs so that first-time visitors will see a personalized CTA (perhaps with a top-of-the-funnel offer) and those already in your database see a different CTA (maybe for content that offers a little more information about your product or service).
E
30) E-book
E-books are a common type of content that many marketers use, often to help generate leads. They are generally a more long-form content type than, say, blog posts, and go into in-depth detail on a subject.
31) Editorial Calendar
It’s like a road map for content creation, showing you what kind of content to create, what topics to cover, which personas to target, and how often to publish to best support your strategy. Maintaining an editorial calendar will keep you more organized and show you any gaps you may have in your content library. It also helps ensure you’re doing the right things for your personas and not going way off-track with the topics you’re covering.
32) Email
In its most basic sense, email stands for “Electronic Mail.” It’s a core component of marketing because it’s a direct connection to a contact’s inbox. However, with great power comes great responsibility, meaning it’s important for marketers to not abuse the email relationship with a contact. It’s far too easy for a contact to click “unsubscribe” after gaining their hard earned trust in your communication.
33) Engagement Rate
A popular social media metric used to describe the amount of interaction — Likes, shares, comments — a piece of content receives. Interactions like these tell you that your messages are resonating with your fans and followers.
34) Evergreen Content
Evergreen content is content that continues to provide value to readers no matter when they stumble upon it. In other words, it can be referenced long after it was originally published, and even then, it’s still valuable to the reader.
Typically, a piece of evergreen content is timeless, valuable, high quality, and canonical or definitive. These posts are typically a content marketer’s best friend because of the tremendous SEO value they provide.
F
35) Facebook
Facebook is a social network you’re likely quite familiar with already — but it has become so much more than just a platform to publish content and gain followers. You can now utilize the awesome targeting options available through Facebook advertising to find and attract brand new contacts to your website and get them to convert on your landing pages … but remember, you still need awesome content to do it.
While it’s a core component of any marketing strategy, it shouldn’t be the only component. Focusing entirely on Facebook (or any other large social channel, for that matter) will only give you a small piece of the inbound marketing pie. And it’s still piping hot, so be careful.
36) Form
The place your page visitors will supply information in exchange for your offer. It’s also how those visitors can convert into precious sales leads. As a best practice, only ask for information you need from your leads in order to effectively follow up with and/or qualify them.
37) Friction
Any element of your website that is confusing, distracting, or causes stress for visitors, causing them to leave your page. Examples of friction-causing elements include dissonant colors, too much text, distracting website navigation menus, or landing page forms with too many fields.
G
38) Google+
Google+ (referred to as “Google Plus”) is a social network that allows you to join and create circles in which you can mix and match family members, friends, colleagues, and fellow industry members. While you can use it much like other social networks — to publish and share content, and generate new leads — it also provides content marketers with tremendous SEO value due to the rising importance of social sharing in search engine algorithms.
H
39) Hashtag
Hashtags are a way for you and your readers to interact with each other on social media and have conversations about a particular piece of content. They tie public conversations on Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram together into a single stream, which users can find by searching for a hashtag, clicking on one, or using a third-party monitoring tool.
The hashtags themselves are simply a keyword phrase, spelled out without spaces, with a pound sign (#) in front of it — like #InboundChat and #ChocolateLovers. You can put these hashtags anywhere in your social media posts.
40) HTML
This is short for HyperText Markup Language, a language used to write web pages. It’s at the core of every web page, regardless the complexity of a site or number of technologies involved, and provides the basic structure of the site — which is then enhanced and modified by other technologies like CSS and JavaScript.
I
41) Inbound Marketing
Inbound marketing refers to marketing activities that draw visitors in, rather than marketers having to go out to get prospects’ attention. It’s all about earning the attention of customers, making the company easy to find online, and drawing customers to the website by producing interesting, helpful content. By aligning the content you publish with your customer’s interests, you naturally attract inbound traffic that you can then convert, close, and delight over time.
42) Inbound Link
An inbound link is a link coming from another site to your own website. “Inbound” is generally used by the person receiving the link.
Websites that receive many inbound links can be more likely to rank higher in search engines. They also help folks receive referral traffic from other websites.
43) Infographic
A highly visual piece of content that is very popular among digital marketers as a way of relaying complex concepts in a simple and visual way.
44) Instagram
Though initially a haven only for younger generations who wanted to post, edit, and share unique-looking photos, Instagram has grown into a premier social network that’s a viable opportunity for content marketers. Many businesses are taking advantage of the site by posting industry related photos that their followers and customers would enjoy seeing.
J
45) JavaScript
JavaScript is a programming language that lets web developers design interactive sites. Most of the dynamic behavior you’ll see on a web page is thanks to JavaScript, which augments a browser’s default controls and behaviors.
Uses for JavaScript include pop-ups, slide-in calls-to-action, security password creation, check forms, interactive games, and special effects. It’s also used to build mobile apps and create server-based applications.
K
46) Key Performance Indicator (KPI)
A type of performance measurement companies use to evaluate an employee’s or an activity’s success. Marketers look at KPIs to track progress toward marketing goals, and successful marketers constantly evaluate their performance against industry standard metrics. Examples of KPIs include CAC (Customer Acquisition Cost), blog traffic sources, and homepage views. Choose KPIs that represent how your marketing and business are performing.
47) Keyword
Sometimes referred to as “keyword phrases,” keywords are the topics that webpages get indexed for in search results by engines like Google, Yahoo, and Bing.
Picking keywords that you’ll optimize a webpage for is a two-part effort. First, you’ll want to ensure the keyword has significant search volume and is not too difficult to rank for. Then, you’ll want to ensure it aligns with your target audience
After deciding the appropriate keywords you want to rank for, you’ll then need to optimize the appropriate pages on your website using both on-page and off-page tactics.
L
48) Landing Page
A landing page is a website page containing a form that is used for lead generation. This page revolves around a marketing offer, such as an e-book or a webinar, and serves to capture visitor information in exchange for the valuable offer. Landing pages are the gatekeepers of the conversion path and are what separates a website visitor from becoming a lead.
A smart inbound marketer will create landing pages that appeal to different personae (plural for persona) at various stages of the buying process. A hefty endeavor no doubt, but one that pays off in spades.
49) Lead
A person or company who’s shown interest in a product or service in some way, shape, or form. Perhaps they filled out a form, subscribed to a blog, or shared their contact information in exchange for a coupon.
Generating leads is a critical part of a prospect’s journey to becoming a customer, and it falls in between the second and third stages of the larger inbound marketing methodology, which you can see below.
Landing pages, forms, offers, and calls-to-action are just a few tools to help companies generate leads.
50) Lead Nurturing
Sometimes referred to as “drip marketing,” lead nurturing is the practice of developing a series of communications (emails, social media messages, etc.) that seek to qualify a lead, keep it engaged, and gradually push it down the sales funnel. Inbound marketing is all about delivering valuable content to the right audience — and lead nurturing helps foster this by providing contextually relevant information to a lead during different stages of the buying lifecycle.
51) LinkedIn
LinkedIn is a business-oriented social networking site. Launched in May 2003, it is mainly used for professional networking. Nowadays, with more than 414 million registered members, LinkedIn is the most popular social network for professionals and one of the top social networks overall. Getting on the platform, developing a completed profile, and networking has helped many a jobseeker find work.
52) Lifecycle Stages
These divisions serve as a way to describe the relationship you have with your audience, and can generally be broken down into three stages: awareness, evaluation, and purchase.
What’s important to understand about each of these stages is that not every piece of content you create is appropriate, depending on what stage your audience might fall in at that moment. That’s why dynamic content is so great — you can serve up content that’s appropriate for whatever stage that particular visitor is in.
53) Lifetime Value (LTV)
A prediction of the net profit attributed to the entire future relationship with a customer. To calculate LTV, follow these steps for a given time-period:
- Take the revenue the customer paid you in that time-period.
- Subtract from that number the gross margin.
- Divide by the estimated churn rate (aka cancellation rate) for that customer.
For example, if a customer pays you $100,000 per year where your gross margin on the revenue is 70%, and that customer type is predicted to cancel at 16% per year, then the customer’s LTV is $437,500.
54) Long-Tail Keyword
A long-tail keyword is a very targeted search phrase that contains three or more words. It often contains a head term, which is a more generic search term, plus one or two additional words that refine the search term. For example:
- Head term: unicorn
- Long-tail keywords: unicorn games online, unicorn costumes for kids,
Long-tail keywords are more specific, which means visitors that land on your website from a long-tail search term are more qualified, and consequently, more likely to convert.
55) LTV:CAC
The ratio of lifetime value (LTV) to customer acquisition cost (CAC). Once you have the LTV and the CAC, compute the ratio of the two. If it costs you $100,000 to acquire a customer with an LTV of $437,500, then your LTV:CAC is 4.4 to 1.
M
56) Marketing Automation
While there’s some overlap with the term “lead nurturing,” marketing automation is a bit different. Think of marketing automation as the platform with associated tools and analytics to develop a lead nurturing strategy. If you’ll let me run with an “art” analogy, marketing automation is the paintbrush, watercolors, and blank canvas. Lead nurturing is the artist that makes it all come together. Like Bob Ross! You can’t paint a happy little nurturing campaign without both.
Bonus: Want to get super-savvy with your marketing automation terminology? Take it to the next level with behavior-based marketing automation. Behavior-based marketing automation refers to a system that triggers emails and other communication based on user activity on and off your site. It enables marketers to nurture leads and send them information only when it is most relevant to their stage in the buying cycle.
57) Microsite
A cross between a landing page and a “regular” website. ElfYourself.com is a great example. Microsites are used when marketers want to create a different online experience for their audience separate from their main website. These sites often have their own domain names and distinct visual branding.
58) Middle of the Funnel
This refers to the stage that a lead enters after identifying a problem. Now they’re looking to conduct further research to find a solution to the problem. Typical middle of the funnel offers include case studies or product brochures — essentially anything that brings your business into the equation as a solution to the problem the lead is looking to solve. Also, if you want to be cool, you can refer to this stage as “MOFU” for short.
59) Mobile Marketing
With mobile search queries officially surpassing desktop queries, now is probably the time to explore mobile marketing. What is it? Well, mobile marketing refers to the practice of optimizing marketing for mobile devices to provide visitors with time- and location- sensitive, personalized information for promoting goods, services, and ideas.
60) Mobile Optimization
Mobile optimization means designing and formatting your website so that it’s easy to read and navigate from a mobile device. This can be done by either creating a separate mobile website or incorporating responsive design in initial site layout. Google’s algorithm now rewards mobile-friendly websites, so if your site isn’t fully optimized for mobile devices, you will likely see a hit to your ranking on mobile searches.
61) Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
The amount of revenue a subscription-based business receives per month. Includes MRR gained by new accounts (net new), MRR gained from upsells (net positive), MRR lost from down-sells (net negative), and MRR lost from cancellations (net loss).
N
62) Native Advertising
A type of online advertising that takes on the form and function of the platform it appears on. Its purpose is to make ads feel less like ads, and more like part of the conversation. That means it’s usually a piece of sponsored content that’s relative to the consumer experience, isn’t interruptive, and looks and feels similar to its editorial environment.
Native advertising can come in many forms, whether it’s radio announcers talking favorably about a product sponsoring the show, or an article about a product or company showing up in your news source.
63) Net Promoter Score (NPS)
A customer satisfaction metric that measures, on a scale of 0-10, the degree to which people would recommend your company to others. The NPS is derived from a simple survey designed to help you determine how loyal your customers are to your business.
To calculate NPS, subtract the percentage of customers who would not recommend you (detractors, or 0-6) from the percent of customers who would (promoters, or 9-10).
Regularly determining your company’s NPS allows you to identify ways to improve your products and services so you can increase the loyalty of your customers.
64) News Feed
A news feed is an online feed full of news sources. On Facebook, the News Feed is the homepage of users’ accounts where they can see all the latest updates from their friends. The news feed on Twitter is called Timeline.
65) No-Follow Link
A no-follow link is used when a website does not want to pass search engine authority to another webpage. It tells search engine crawlers not to follow or pass credit to linked websites as-a-way to avoid association with spammy content or inadvertently violating webmaster guidelines. To varying degrees, the no-follow attribute is recognized by all major search engines, like Google, Yahoo, and Bing. Not all links (and linking domains) are created equal, and a no-follow attribute helps avoid any foul play.
O
66) Offer
Offers are content assets that live behind a form on a landing page. Their primary purpose is to help marketers generate leads for your business. There are many different types of offers you could create, including e-books, checklists, cheat sheets, webinars, demos, templates, and tools.
67) On-Page Optimization
This type of SEO is based solely on a webpage and the various elements within the HTML (see “H” if you skipped here directly). Ensuring that key pieces of the specific page (content, title tag, URL, and image tags) include the desired keyword will help a page rank for that particular phrase.
68) Off-Page Optimization
Off-page SEO refers to incoming links and other outside factors that impact how a webpage is indexed in search results. Factors like linking domains and even social media play a role in off-page optimization. The good news is that it’s powerful; the not so good news is that it’s mostly out of an inbound marketer’s control. The solution? Create useful, remarkable content and chances are people will share and link to it.
P
69) Page View
A request to load a single web page on the internet. Marketers use them to analyze their website and to see if any change on the webpage results in more or fewer page views.
70) Pay-per-Click (PPC)
The amount of money spent to get a digital advertisement clicked. Also an internet advertising model where advertisers pay a publisher (usually a search engine, social media site, or website owner) a certain amount of money every time their ad is clicked. For search engines, PPC ads display an advertisement when someone searches for a keyword that matches the advertiser’s keyword list, which they submit to the search engine ahead of time.
PPC ads are used to direct traffic to the advertiser’s website, and PPC is used to assess the cost effectiveness and profitability of your paid advertising campaigns.
There are two ways to pay for PPC ads:
- Flat rate: where the advertiser and publisher agree on a fixed amount that will be paid for each click. Typically this happens when publishers have a fixed rate for PPC in different areas on their website.
- Bid-based: where the advertiser competes against other advertisers in an advertising network. In this case, each advertiser sets a maximum spend to pay for a given ad spot, so the ad will stop appearing on a given website once that amount of money is spent. It also means that the more people that click on your ad, the lower PPC you’ll pay and vice versa.
71) Pinterest
Pinterest is a visual social network typically used by ecommerce marketers, but not without its fair share of top-notch B2B and B2C content marketers. Businesses and consumers alike use the website to post images and photos they like so fellow users can repin (share) that content.
72) PPC
PPC, (or Pay-Per-Click) is an advertising technique in which an advertiser puts an ad in an advertising venue (like Google AdWords or Facebook), and pays that venue each time a visitor clicks on the ad.
Q
73) Qualified Lead
A contact that opted in to receive communication from your company, became educated about your product or service, and is interested in learning more.
74) QR Code
A QR code (abbreviated from Quick Response code) is a specific matrix barcode (or two-dimensional code) that is readable by dedicated QR barcode readers and camera telephones. The code consists of black modules arranged in a square pattern on a white background. The information encoded may be text, URL, or other data. It also starts with “Q,” which is a rarity with marketing-related terms.
R
75) Responsive Design
This is the practice of developing a website that adapts accordingly to how someone is viewing it. Instead of building a separate, distinct website for each specific device it could be viewed on, the site recognizes the device that your visitor is using and automatically generates a page that is responsive to the device the content is being viewed on — making websites always appear optimized for screens of any dimension.
76) Return on Investment (ROI)
A performance measure used to evaluate the efficiency and profitability of an investment, or to compare the efficiency and profitability of multiple investments. The formula for ROI is: (Gain from Investment minus Cost of Investment), all divided by (Cost of Investment). The result is expressed as a percentage or ratio. If ROI is negative, then that initiative is losing the company money. The calculation can vary depending on what you input for gains and costs.
Today, marketers want to measure the ROI on every tactic and channel they use. Many facets of marketing have pretty straightforward ROI calculations (like PPC), but others are more difficult
77) Retweet
A re-posting of a tweet posted by another user on Twitter. Retweets look like normal tweets except for the retweet icon. They can be done in three ways:
1) You can retweet an entire tweet by clicking the retweet button.
2) You can post a new tweet that includes your own commentary. In a new tweet, which also features the original tweet. It means you’ve pressed the rotating arrow icon to retweet a post, and then added a comment in the text box provided. We prefer this method of retweeting because it allows you to add your own thoughts. (Note: The retweet takes up 24 characters, leaving you with 116 characters for the comment.)
3) You can post a new tweet that includes your own commentary in addition to the information you’re retweeting. The formula is this: Your own commentary + RT + the original tweeter’s Twitter handle + colon + the exact text from their original tweet. This method of retweeting allows you to add your own thoughts, but with a very limited character count.
When you see “Please RT” in someone’s tweet, it means they are requesting that their followers retweet that tweet to spread awareness.
S
78) Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
The practice of enhancing where a webpage appears in search results. By adjusting a webpage’s on-page SEO elements and influencing off-page SEO factors, an inbound marketer can improve where a webpage appears in search engine results.
There are a ton of components to improving the SEO of your site pages. Search engines look for elements including title tags, keywords, image tags, internal link structure, and inbound links — and that’s just to name a few. Search engines also look at site structure and design, visitor behavior, and other external, off-site factors to determine how highly ranked your site should be in the search engine results pages.
79) Sender Score
An email marketing term that refers to a reputation rating from 0-100 for every outgoing mail server IP address. Mail servers will check your Sender Score before deciding what to do with your emails. A score of over 90 is good.
80) Service Level Agreement (SLA)
For marketers, an SLA is an agreement between a company’s sales and marketing teams that defines the expectations Sales has for Marketing and vice versa. The Marketing SLA defines expectations Sales has for Marketing with regards to lead quantity and lead quality, while the Sales SLA defines the expectations Marketing has for Sales on how deeply and frequently Sales will pursue each qualified lead.
SLAs exist to align sales and marketing. If the two departments are managed as separate silos, the system fails. For companies to achieve growth and become leaders in their industries, it is critical that these two groups be properly integrated.
81) Small-to-Medium Business (SMB)
Usually defined as companies that have between 10 and 500 employees.
82) Smarketing
A fun phrase used to refer to the practice of aligning Sales and Marketing efforts. In a perfect world, marketing would pass off tons of fully qualified leads to the sales team, who would then subsequently work every one of those leads enough times to close them 100% of the time. But since this isn’t always how the cookie crumbles, it’s important for Marketing and Sales to align efforts to impact the bottom line the best they can through coordinated communication.
83) Snapchat
A social app that allows users to send and receive time-sensitive photos and videos known as “snaps,” which are hidden from the recipients once the time limit expires. (Note: Images and videos still remain on the Snapchat server). Users can add text and drawings to their snaps and control the list of recipients in which they send them to.
A Snapchat story is a string of Snapchats that lasts for 24 hours. Users can create stories to be shared with all Snapchatters or just a customized group of recipients.
84) Social Media
Social media is media designed to be disseminated through social interaction, created using highly accessible and scalable publishing techniques. Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, LinkedIn and Google+ are examples of social media networks that one can join for personal or business use. Social Media is a core component of Inbound, as it provides marketers with additional channels to spread reach, increase growth, and reach business goals.
85) Social Proof
Social proof refers to a psychological phenomenon in which people seek direction from those around them to determine how they are supposed to act or think in a given situation. It’s like when you see a really long line outside a nightclub and assume that club is really good because it’s in such high demand. In social media, social proof can be identified by the number of interactions a piece of content receives or the number of followers you have. The idea is that if others are sharing something or following someone, it must be good.
86) Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
Any software that is hosted by another company, which stores your information in the cloud. Examples: HubSpot, Salesforce, IM clients, and project management applications.
T
87) Top of the Funnel
Sometimes called “TOFU”, top of the funnel refers to the very first stage of the buying process. Leads at this stage are just identifying a problem that they have and are looking for more information. As such, an inbound marketer will want to create helpful content that aids leads in identifying this problem and providing next steps toward a solution.
88) Twitter
For the sake of creativity, I’ll define Twitter in 140 characters or less: “Twitter is a platform that allows users to share 140-character long messages publicly. User can follow one another and be followed back.”
U
89) Unique Visitor
A person who visits a website more than once within a period of time. Marketers use this term in contrast with overall site visits to track the amount of traffic on their website. If only one person visits a webpage 30 times, then that web page has one UV and 30 total site visits.
90) URL
This is short for Uniform Resource Locator. I honestly didn’t know that before writing this definition. Basically, this is the address of a piece of information that can be found on the web such as a page, image, or document (ex. http://www.huspot.com). URLs are important for on-page SEO, as search engines scour the included text when mining for keywords. If a keyword you’re looking to get indexed for is in the URL, you’ll get brownie points from search engines (but no real brownies, unfortunately).
91) User Experience (UX)
The overall experience a customer has with a particular business, from their discovery and awareness of the brand all the way through their interaction, purchase, use, and even advocacy of that brand. To deliver an excellent customer experience, you have to think like a customer, or better, think about being the customer.
92) User Interface (UI)
A type of interface that allows users to control a software application or hardware device. A good user interface provides a user-friendly experience by allowing the user to interact with the software or hardware in an intuitive way. It includes a menu bar, toolbar, windows, buttons, and so on.
V
93) Viral Content
This term is used to describe a piece of content that has become wildly popular across the web through sharing.
W
94) Website
A website is a set of interconnected webpages, usually including a homepage, generally located on the same server, and prepared and maintained as a collection of information by a person, group, or organization. An inbound marketer should structure a website like a dynamic, multi-dimensional entity that can be used to attract relevant website visitors, convert those visitors into leads, and close those leads into customers. Otherwise, it’s just a brochure — and let’s be honest — could you really use another brochure?
95) Word-of-Mouth (WOM)
The passing of information from person to person. Technically, the term refers to oral communication, but today it refers to online communication, as well. WOM marketing is inexpensive, but it takes work and involves leveraging many components of inbound marketing like product marketing, content marketing, and social media marketing.
96) Workflow
A workflow is another way to describe a lead nurturing campaign. It’s a set of triggers and events that move a lead through the nurturing process. A workflow can also serve other purposes, such as adjust contact properties on a lead record based on certain conditions, or adding a contact record to a certain list. Regardless of how you use it, workflows can be a very powerful asset in an inbound marketing strategy.
X
97) XML Sitemap
We couldn’t leave “X” out of the party! An XML sitemap is a file of code that lives on your web server and lists all of the relevant URLs that are in the structure of your website. It’s kind of like a “floor plan” for the site, which especially comes in handy whenever the site gets changed. It also helps search engine web crawlers determine the structure of the site so they can crawl it more intelligently.
Sitemaps don’t guarantee all links will be crawled, and being crawled does not guarantee indexing. However, a sitemap is still the best insurance for getting a search engine to learn about your entire site. It’s sort of like saying “Hey, Google — check out this fine website.”
Y
98) YouTube
YouTube is a video-sharing website on which users can upload, share, and view videos. Three former PayPal employees created YouTube in February 2005. In November 2006, YouTube, LLC was bought by Google Inc. for $1.65 billion, and is now operated as a subsidiary of Google. YouTube is the largest video-sharing site in the world and you’re probably on it now instead of finishing up this post.
Z
99) Zilch
We couldn’t think of anything for “Z.”
8 Can’t-Miss Off-Page SEO Strategies to Build Your Online Reputation

What is off-page SEO?
Off-page SEO is the act of optimizing your brand’s online and offline footprint through the use of content, relationships, and links to create an optimal experience for prospects and search engine crawl bots. It typically leads to gradual increases in positive brand mentions, search rankings, traffic to your site, and conversions.
Sounds fairly straightforward, right?
Well, for the attorney seated in front of me in my kid’s elementary school lunchroom, I might as well have just told him the earth is flat.
“That makes no sense to me,” he said, pushing his chin forward and tilting his head, as if waiting for me to admit that I was pulling his leg. “You mean, there’s all this stuff [an SEO] does on my site? And there is stuff that we — me, my team and [the SEO] — should be doing off our site as well? That’s like telling me, ‘It’s not enough that you live and pay for a nice house in a gated community. You also need to guard the gate to the community and pick up trash along the road leading up to your driveway.'”
His example could not have been more apt.
“Not caring about off-site SEO is like having that great house in the gated community, but none of your friends want to visit because they’ve heard from others that it smells like vomit on the inside, and no one they talk to can either confirm or deny it.”

By imagining your website as a home you’d like people to visit, it’s easier to see the value of off-site SEO.
I continued: “It’s not enough to only care about your website/brand or your house/neighborhood; you must always be working to enhance its reputation to ensure others will desire to visit/learn more about it.”
He saw the light.
“So basically we do off-site SEO to ensure the work we do onsite and as a brand are most effective?” he asked.
Exactly!
Why your brand cannot afford to ignore off-site SEO
In the SEO world, we don’t need to be convinced of the value of off-page SEO.
We know that well before people seek our brands out, they have formed an opinion of it based on reviews, comments from friends, family members, or online acquaintances, and whatever information we can glean online or offline (apart from your website).
Therefore, we’d be fools to disavow making off-page SEO a priority, given how important it is.
However, the more common mistake — among SEOs at least — is to see off-page SEO through only the prism of link building, which, while important, is not the be-all and end-all of off-page SEO.
That is, in working to build your brand’s off-page SEO prowess, links are certainly a benefit, not the goal.
Think of it this way:
- Goal of off-page SEO: To accumulate positive signals and interactions for your brand, with the hope of those factors being a net positive.
- Benefit(s) of off-page SEO: Brand mentions, positive reviews, links, etc.
So while it’s important to think of links when making off-page SEO a priority, it’s also vital that you (a) view them in context (important but not singularly so) and (b) give priority to the host of factors that lead to off-page SEO providing a boost for your brand.
Those factors include, but are not limited to, creating an excellent, worthwhile product or service; guest posting on popular, relevant blogs; building relationships with influencers; earning positive press; capturing positive reviews and responding to negative reviews; and monitoring mentions of your brand, to name a few.
Because our goal is to create a post that’s accessible, interesting and immediately useful, we’ll break down what we think are 8 key areas worth focusing on for off-page SEO under three umbrellas:
- Brand
- Audience
- Content
The intention is to provide a prism through which you can more easily categorize your efforts and a framework by which you can make those efforts a reality.

Brand
“No amount of SEO in the world can help a crappy product or service (at least not for long).” This is a sentence I frequently utter to folks who refuse to prioritize what they offer in favor of trying to put lipstick on a pig.
#1: Create a 10X product or service
When your product or service is recognized as the best in its class, your job as SEO becomes much, much easier.
That’s because both online and offline, people are likely saying great things about the product and brand, which leads to visits to your website, positive reviews on third-party sites, and increased sales of the product.
This only occurs, however, if you focus first and foremost on creating the best product you can.
Easier said than done, I know.
Here’s a great place to start, depending upon where your product/service is in the evolution cycle:
- Existing product: Deliver the goods on features customers would most benefit from based on requests and complaints online regarding competing products.
- New product: Focus on the most essential benefits your new product can provide to the prospective audience. When you do this, you remove objections and features present themselves.
#2: Customer service
No one who’s watched the United Airlines meltdown needs to be sold on the value of customer service as an effective asset for off-site SEO. The brand will be paying for that epic disaster for years as millions of folks continue to share the video and images of the event.
It’s not hard to imagine how poor customer service has made the brand’s SEO and PR teams’ reputation management efforts a nightmare.
For your brand, focus on a singular goal: Leaving everyone your brand/brand spokespeople comes into contact with — online or offline — feeling as though the interaction could not have been more positive.
For example, at in-person events, make sure staffers wear a smile, empathetically interact with everyone they meet, and go out of their way to answer questions or provide general help. It also means ensuring any content you create leaves people feeling good about your brand.

It’s unlikely this billboard was much of an off-page SEO benefit to SouthBendOn.com.
# 3: Focus on web searchers’ intent
Turns out the old cliche that “you attract more flies with honey than vinegar” is very relevant to SEO. People are typically more willing to buy and use your products and services if they can first find them.
A lot of times, our products and services fail to live up to their full potential because we aren’t matching our offering to the needs of our prospective audiences.
A great example of this is creating and sharing content without keywords the audience might be using to look for a similar product.
In addition to matching titles, descriptions, and keyword phrases to searcher’s intent, make sure you focus on where the content is shared and discussed.
It also starts with putting the needs of the audience first.
“For uncovering searcher intent…[s]earch, refine, broaden queries, talk to people, read discussion threads, have empathy,” wrote Rand Fishkin in a recent tweet.
Use Google Autosuggest, Keywordtool.io, Keyword Explorer, and Answerthepublic.com to get in front of what it is people are looking for online relative to your product or service.
Audience
The better you know your audience, the more easily you can interact with, share with, and learn from them.
What does this have to do with off-page SEO? Everything.
Next to no one wakes up and decides to interact with your brand.
#4: Have a responsive social media presence
A typical search comes about because a person has an unmet need (e.g., “where is the nearest pizza joint?”) or has a question they’d like answered (e.g., “how tall is the biggest building in Tokyo?”).
After using Google Autosuggest to find the answer, they’re likely to visit social media to learn more, ask questions, and interact with their friends, family members, and acquaintances.
You see where we’re going here, right?
Social media must be an invaluable component of your off-page SEO strategy.
It’s much easier than most brands think, too:
- Be there: If you have a social media account, make sure someone is monitoring it and can answer questions and respond to comments in a timely fashion.
- Be human: People online expect genuine interaction, not robotic responses or constant brand promotion.
- Be proactive: One of the best things you can do to help your brand is to use social media to be seen as a resource for the online community in the vertical you serve. Even if someone asks a question about a product or service you don’t offer or that is offered by a competitor, don’t be afraid to chime in and offer praise when due.
As you can see, the price of unresponsiveness on social media negatively impacts far more than SEO:
#5: Build connections with social media/online influencers
When people say “Social media does nothing for my brand,” most SEOs must think, “Oh, but how wrong you are.”
Whether it’s the largely unmeasurable dark traffic social sends to your site or the connections with a base of people who could be customers or supporters at some point, social media can be an asset for any brand, if used wisely.
For off-page SEO, one of the biggest benefits of social is the ability to create and nurture lasting relationships with influencers, those people with huge reach in the way of name recognition, myriad followers and fans, and connections with numerous high-ranking websites.
They’re also typically very much connected with other influencers.
As we see in the image below, even if Google isn’t using social signals to help determine rankings, the interplay of influencers and the sites they represent, like, and visit makes being on their radar a positive.
Image source
An effective strategy for enlisting the help of influencers to boost your off-page SEO is to get to know them in person, at events, and online via group chats/tweets and such, which puts you on their radar without much heavy lifting on your part.
Then, in the future, when you do create and share content, they’re more likely to recognize you and your brand and might share the content themselves.
Even better, later on, after you’ve developed a stronger relationship, you might even collaborate on a piece of content — for their site, your site, or a publisher such as an online magazine.
#6: Recommit to frequenting forums and discussion boards, and comment blogging
Want to get noticed by your desired audience and the influencers they follow?
Visit the most popular blogs in your vertical, and leave comments. In recent years, comment blogging has fallen off in popularity, in large part because comment spam led to most blogs no-following their links.
For the purpose of off-page SEO, links are less of a priority.
Your goal is simply to be where the action is and to leave a thoughtful comment that might catch the eye of the blogger, the platform’s editor, and any influencers who might be reading the content.
The same applies for sites like Reddit and Quora, where you can follow topics specifics to your brand or vertical and quickly get noticed for being knowledgeable, thoughtful, and empathetic in answering others’ questions or helping to drive discussion.
The SEO subreddit is very popular, frequented by many of the big names in SEO.
The relationships formed on these platforms have a way of paying huge dividends and can be invaluable for off-page SEO and reputation management.
Often someone notices your comments on one of these platforms, starts following you there, and then later does a Google or LinkedIn search to learn about you or your brand, which ultimately leads them to your website, where they might sign up for your newsletter or subscribe to your blog.
#7: Quit guest blogging for links
You read that right.
Instead of guest blogging solely for links, use this tactic to help you build a rapport with some of the top publishers, editors, influencers, and brands online.
If done correctly, the links do come. But as long as you make links the priority, whereby it’s obvious that you’re looking for a transactional relationship as opposed to one that is mutually beneficial, the tougher it’ll be for you to use guest blogging effectively for off-page SEO.
Read, leave comments on their blogs, and connect with the top publishers in your vertical — or publishers that cover your vertical. Once you have developed a rapport and, hopefully, have a reputation for creating quality content, inquire about creating a guest post for the platform, assuming that option is available.
Even if that door doesn’t open, you’ll be able to hone your pitch and eventually get a foot in the door with other publishers.
Remember, too, that your website is but one tiny fish in a vast ocean of options. You need to connect with others in many places off-site to build the reach and influence that’ll drive attention and visits to your site, which is where guest blogging can big a huge asset.
Your brand’s success depends upon a lot of factors outside your website. Image source
“Should you do guest posting for SEO? As a primary objective, I’d say no. But… reality is that the indirect impact remains very powerful,” wrote Stone Temple Consulting’s Eric Enge. “There is nothing like building your reputation and visibility to cause people to want more of your content. You get to build up your own audience, and ultimately some of these people will find their way to your site, find great content there, and link to it.”
Content
When most people say, think, or write “content,” they most often think of text, images, videos, and information shared via social media.
In reality, content represents the entirety of the experience your brand designs, creates, and shares online and offline, from logos and tag lines to personnel, phone calls, signage, blog text, images, videos, etc.
If a prospect or customer can interacts with it, you’d better believe it’s content.
And before you offer up, “Well, Ronell, what if one of my staffers has mustard on her shirt in a video we post online?” (Trust me, someone would ask that.) “Is that content, too?” Yes, that faux pas is part of the content experience a prospect or customer could have with your brand.
In fact, it’s the sort of thing that can lead to someone seeing your company as not having all of its ducks in a row, injuring your reputation in the process.
#8: Experiment with content types
But don’t fret. When it comes to off-site SEO, the main thing I want you to focus on with regard to content is to see beyond text.
I’m a writer. I love words.
As a newspaper reporter, I always argued with my editor when he said “Words without images lead to words getting ignored. Images sell.”
The same for video. People eat it up.
You’ve no doubt heard that mobile is gobbling up the world as I write this. Well, guess what those untold millions are doing on their mobile devices?
Largely consuming videos, which are expected to account for 85% of the content being shared online by 2019. Snapchat, Instagram, or Facebook Live, anyone?
Image source
Videos and images can be a huge boon to your brand’s off-page SEO, largely because they can both be a low-investment/high potential vehicle used to drive awareness and traffic back to your site, enhancing your off-page reputation in the process.
A few low-cost, low-effort ways to use video and images include:
- Post how-to videos on YouTube, which is the second-most visited website in the world and the #2 search engine behind parent company Google. What’s more, popular videos can and do rank in the SERPs.
- Share daily musings or recaps of distillations of recent events via Facebook Live
- Snap meeting or office funnies via Snapchat
- Compose image albums on Imgur, Flickr, and other popular photo-sharing sites
- Tweet videos of interesting things you notice throughout the day
Video and images are great way to show some personality and make your brand feel human, real, and alive to people who might not have heard of your company, or who’ve only recently discovered it.
They can also work wonders for your off-site SEO.
For example, say your brand has found that customers who visit your white papers have an increased likelihood of becoming customers. You might shoot video interviews of the subjects or clients featured in the most popular websites, then post the videos to YouTube, in addition to sharing them with the clients to post on their site and disseminate via social media.
This increases the likelihood of even more people seeing the videos and wanting to learn more about your brand.
It’s time to think holistically
The complete list of off-site SEO tactics that can bring your brand success contains far more than eight elements.
Our goal with this post is to spur you to think beyond what’s comfortable or convenient, and instead consider what’s (a) doable in a reasonable amount of time and a reasonable degree of effort, and that (b) has the potential to yield a significant amount of success.
We’re convinced that a brand who works diligently to deploy the tactics listed above will be better able to thrive.
About Ronell Smith — Ronell Smith is a Moz Associate and business strategist who enjoys helping businesses create a user experience their customers will recognize, appreciate and reward them for with their business.



